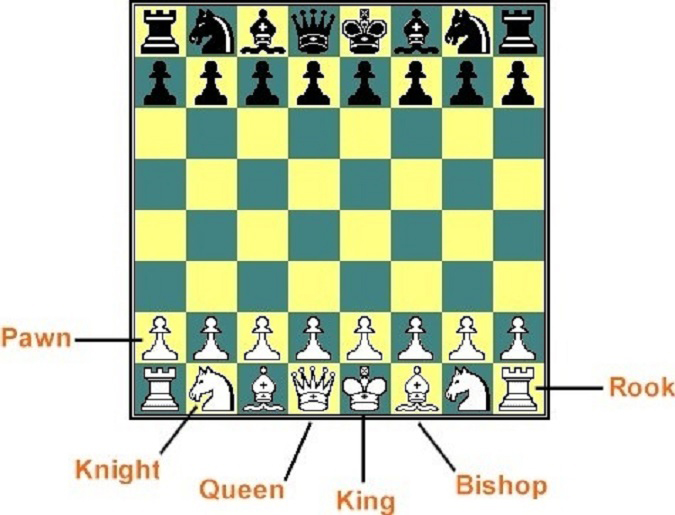
Today we will look at algebraic notation. It is a significant part of chess. The World Chess Federation’s (FIDE) rules stipulate that in competitive chess, what we refer to as tournament chess, it is compulsory for a player to record his/her move. In addition to such a regulation, I improved my chess by replaying grandmaster games through notation. When readers learn notation, they can do the same.
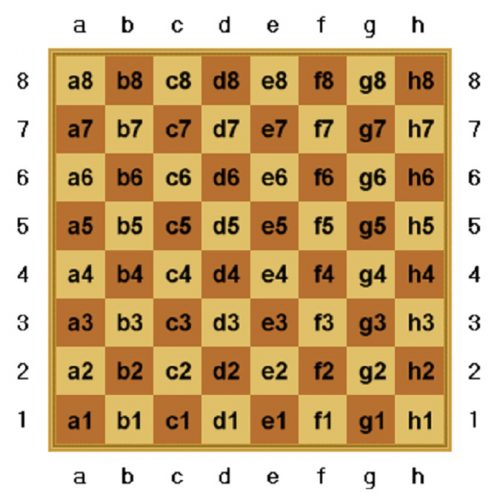
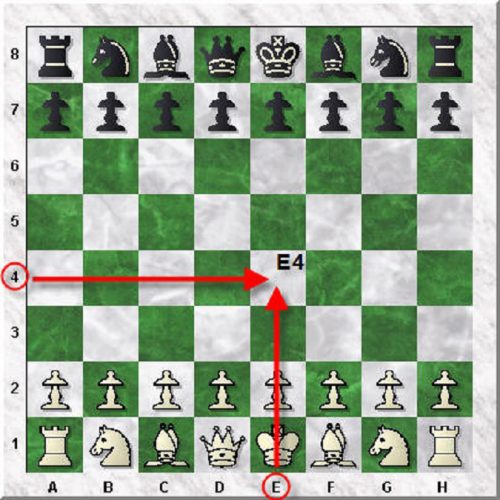
Algebraic notation is a system of notation in which each square on the board is identified by a grid system. Each file is assigned a letter and each rank a number. In this way every square is uniquely identified by a combination of letter and number. The files from left to right are lettered from a to h (see diagram), and the ranks numbered 1 to 8 working from bottom to top. In full algebraic notation, a move is written down by giving the sign or symbol of the piece, its initial square and its final square. The pawns are not represented by any signs or symbols and a pawn’s move is shown by writing down the two squares on which the pawn begins and ends its move. For example, e2-e4. But in modern chess language, this notation has been shortened to e4. Nowadays, only the finishing square is required. Captures are indicated by an x. A check is shown by a plus sign +, double check is demonstrated by two plus signs ++ and checkmate is shown by a number sign # or simply mate. The symbols for castling are zero dash zero 0-0 for the kingside, and zero dash zero dash zero 0-0-0 for the queenside. We have not yet discussed castling, but we will get to that. Castling means placing the King in a safety net. The aim of chess is to break open that safety net and render him powerless.
Years ago, a type of notation was used that was referred to as descriptive notation. I learnt chess in the 1970s when only descriptive notation existed. But algebraic notation has several advantages over descriptive. It is more concise, less open to ambiguity and internationally understood. Its superiority is so great that from 1980 it was the only system of notation officially recognized by FIDE.